Opportunity Reaches ‘Perseverance Valley’ Precipice – Ancient Fluid Carved Gully on Mars
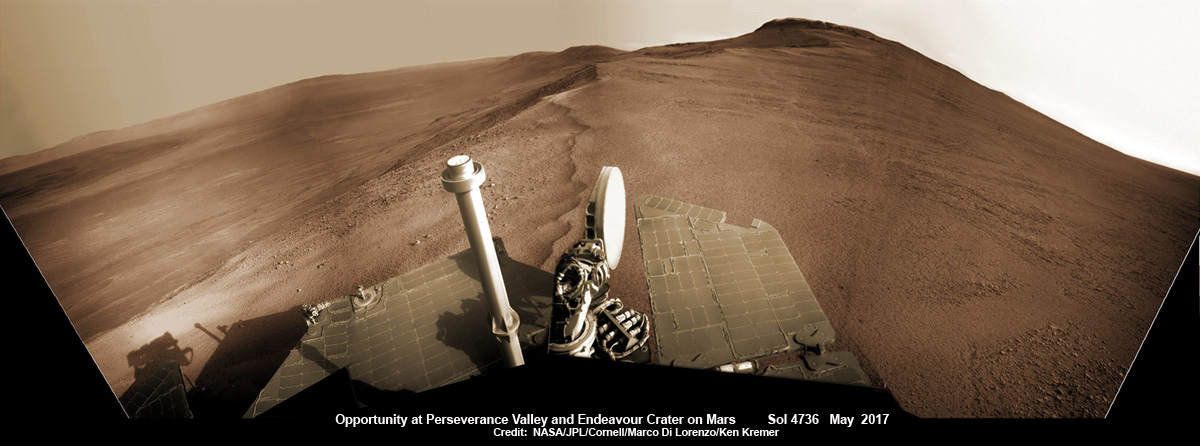


Opportunity rover looks south from the top of Perseverance Valley along the rim of Endeavour Crater on Mars in this partial self portrait including the rover deck and solar panels. Perseverance Valley descends from the right and terminates down near the crater floor. This navcam camera photo mosaic was assembled from raw images taken on Sol 4736 (20 May 2017) and colorized. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
Now well into her 13th year roving the Red Planet, NASA’s astoundingly resilient Opportunity rover has arrived at the precipice of “Perseverance Valley” – overlooking the upper end of an ancient fluid-carved valley on Mars “possibly water-cut” that flows down into the unimaginably vast eeriness of alien Endeavour crater.
Opportunity’s unprecedented goal ahead is to go ‘Where No Rover Has Gone Before!’
In a remarkable first time feat and treat for having ‘persevered’ so long on the inhospitably frigid Martian terrain, Opportunity has been tasked by her human handlers to drive down a Martian gully carved billions of years ago – by a fluid that might have been water – and conduct unparalleled scientific exploration, that will also extend into the interior of Endeavour Crater for the first time.
No Mars rover has done that before.
“This will be the first time we will acquire ground truth on a gully system that just might be formed by fluvial processes,” Ray Arvidson, Opportunity Deputy Principal Investigator of Washington University in St. Louis, told Universe Today.
“Opportunity has arrived at the head of Perseverance Valley, a possible water-cut valley here at a low spot along the rim of the 22-km diameter Endeavour impact crater,” says Larry Crumpler, a rover science team member from the New Mexico Museum of Natural History & Science.
NASA’s unbelievably long lived Martian robot reached a “spillway” at the top of “Perseverance Valley” in May after driving southwards for weeks from the prior science campaign at a crater rim segment called “Cape Tribulation.”
“The next month or so will be an exciting time, for no rover has ever driven down a potential ancient water-cut valley before,” Crumpler gushes.
“Perseverance Valley” is located along the eroded western rim of gigantic Endeavour crater – as illustrated by our exclusive photo mosaics herein created by the imaging team of Ken Kremer and Marco Di Lorenzo. The mosaics show the “spillway” as the entry point to the ancient valley.

NASA’s Opportunity rover acquired this Martian panoramic view from a promontory that overlooks Perseverance Valley below – scanning from north to south. It is centered on due East and into the interior of Endeavour crater. Perseverance Valley descends from the right and terminates down near the crater floor in the center of the panorama. The far rim of Endeavour crater is seen in the distance, beyond the dark floor. Rover deck and wheel tracks at right. This navcam camera photo mosaic was assembled from raw images taken on Sol 4730 (14 May 2017) and colorized. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com/Marco Di Lorenzo
“Investigations in the coming weeks will “endeavor” to determine whether this valley was eroded by water or some other dry process like debris flows,” explains Crumpler.
“It certainly looks like a water cut valley. But looks aren’t good enough. We need additional evidence to test that idea.”
The valley slices downward from the crest line through the rim from west to east at a breathtaking slope of about 15 to 17 degrees – and measures about two football fields in length!
Huge Endeavour crater spans some 22 kilometers (14 miles) in diameter on the Red Planet. Perseverance Valley slices eastwards at approximately the 8 o’clock position of the circular shaped crater. It sits just north of a rim segment called “Cape Byron.”
Why go and explore the gully at Perseverance Valley?
“Opportunity will traverse to the head of the gully system [at Perseverance] and head downhill into one or more of the gullies to characterize the morphology and search for evidence of deposits,” Arvidson elaborated.
“Hopefully test among dry mass movements, debris flow, and fluvial processes for gully formation. The importance is that this will be the first time we will acquire ground truth on a gully system that just might be formed by fluvial processes. Will search for cross bedding, gravel beds, fining or coarsening upward sequences, etc., to test among hypotheses.”
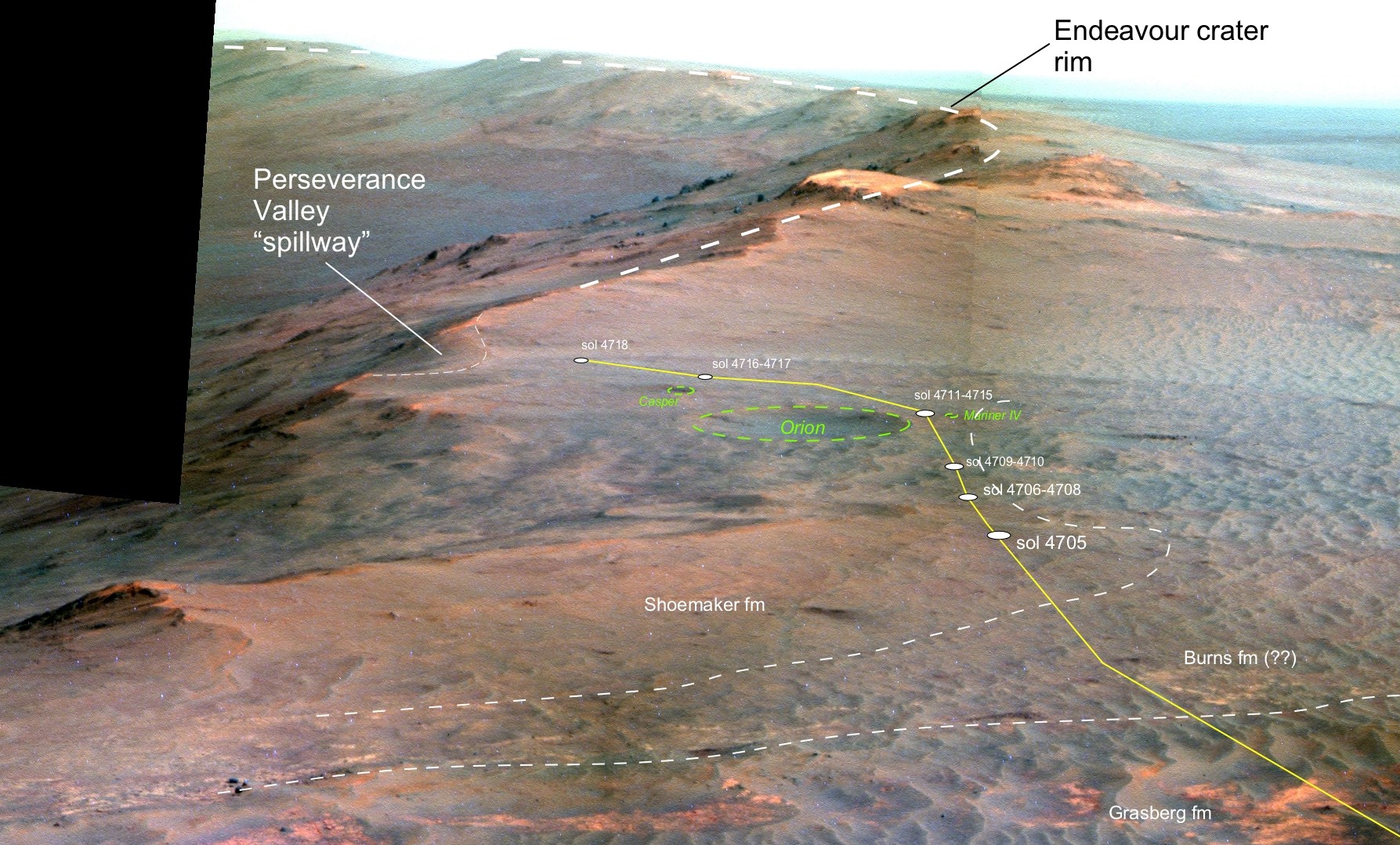
Perspective view of Opportunity’s traverse along Endeavour crater rim over the last few weeks towards the Perseverance Valley “spillway” on Mars during Spring 2017. The entry point for the planned drive back into the crater is visible as the low notch just to the left (east) of the current (sol 4718) rover position. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/NMMNH /Larry Crumpler
Exploring the ancient valley is the main science destination of the current two-year extended mission (EM #10) for the teenaged robot, that officially began Oct. 1, 2016. It’s just the latest in a series of extensions going back to the end of Opportunity’s prime mission in April 2004.
What are the immediate tasks ahead that Opportunity must accomplish before descending down the gully to thoroughly and efficiently investigate the research objectives?
In a nutshell, extensive imaging from a local high point promontory to create a long-baseline 3 D stereo image of the valley and a “walk-about” to assess the local geology.
The rover is collecting images from two widely separated points at a dip at the valley spillway to build an “extraordinarily detailed three-dimensional analysis of the terrain” called a digital elevation map.
“Opportunity has been working on a panorama from the overlook for the past couple of sols. The idea is to get a good overview of the valley from a high point before driving down it,” Crumpler explains.
“But before we drive down the valley, we want to get a good sense of the geologic features here on the head of the valley. It could come in handy as we drive down the valley and may help us understand some things, particularly the lithology of any materials we find on the valley floor or at the terminus down near the crater floor.”
“So we will be doing a short “walk-about” here on the outside of the crater rim near the “spillway” into the valley.”
“We will drive down it to further assess its origin and to further explore the structure and stratigraphy of this large impact crater.”
The six wheeled rover landed on Mars on January 24, 2004 PST on the alien Martian plains at Meridiani Planum – as the second half of a stupendous sister act.
Expected to last just 3 months or 90 days, Opportunity has now endured nearly 13 ½ years or an unfathomable 53 times beyond the “warrantied” design lifetime.
Her twin sister Spirit, had successfully touched down 3 weeks earlier on January 3, 2004 inside 100-mile-wide Gusev crater and survived more than six years.
Opportunity has been exploring Endeavour almost six years – since arriving at the humongous crater in 2011. Endeavour crater was formed when it was carved out of the Red Planet by a huge meteor impact billions of years ago.
“Endeavour crater dates from the earliest Martian geologic history, a time when water was abundant and erosion was relatively rapid and somewhat Earth-like,” explains Crumpler.
Exactly what the geologic process was that carved Perseverance Valley into the rim of Endeavour Crater billions of years ago has not yet been determined, but there are a wide range of options researchers are considering.
“Among the possibilities: It might have been flowing water, or might have been a debris flow in which a small amount of water lubricated a turbulent mix of mud and boulders, or might have been an even drier process, such as wind erosion,” say NASA scientists.
“The mission’s main objective with Opportunity at this site is to assess which possibility is best supported by the evidence still in place.”
Extensive imaging with the mast mounted pancam and navcam cameras is currently in progress.
“The long-baseline stereo imaging will be used to generate a digital elevation map that will help the team carefully evaluate possible driving routes down the valley before starting the descent,” said Opportunity Project Manager John Callas of JPL, in a statement.
“Reversing course back uphill when partway down could be difficult, so finding a path with minimum obstacles will be important for driving Opportunity through the whole valley. Researchers intend to use the rover to examine textures and compositions at the top, throughout the length and at the bottom, as part of investigating the valley’s history.”
The team is also dealing with a new wheel issue and evaluating fixes. The left-front wheel is stuck due to an actuator stall.
“The rover experienced a left-front wheel steering actuator stall on Sol 4750 (June 4, 2017) leaving the wheel ‘toed-out’ by 33 degrees,” the team reported in a new update.
Thus the extensive Pancam panorama is humorously being called the “Sprained Ankle Panorama.” Selected high-value targets of the surrounding area will be imaged with the full 13-filter Pancam suite.
After reaching the bottom of Perseverance Valley, Opportunity will explore the craters interior for the first time during the mission.
“Once down at the end of the valley, Opportunity will be directed to explore the crater fill on a drive south at the foot of the crater walls,” states Crumpler.
As of today, June 17, 2017, long lived Opportunity has survived over 4763 Sols (or Martian days) roving the harsh environment of the Red Planet.
Opportunity has taken over 220,800 images and traversed over 27.87 miles (44.86 kilometers) – more than a marathon.
As of Sol 4759 (June 13, 2017), the solar array energy production was 343 watt-hours with an atmospheric opacity (Tau) of 0.842 and a solar array dust factor of 0.529.
See our updated route map below. It shows the context of the rovers over 13 year long traverse spanning more than the 26 mile distance of a Marathon runners race.
The rover surpassed the 27 mile mark milestone on November 6, 2016 (Sol 4546).

NASA’s Opportunity rover acquired this Martian panoramic view from a promontory that overlooks Perseverance Valley below – scanning from north to south. It is centered on due East and into the interior of Endeavour crater. Perseverance Valley descends from the right and terminates down near the crater floor in the center of the panorama. The far rim of Endeavour crater is seen in the distance, beyond the dark floor. Rover deck and wheel tracks at right. This navcam camera photo mosaic was assembled from raw images taken on Sol 4730 (14 May 2017) and colorized. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com/Marco Di Lorenzo
The power output from solar array energy production is currently 343 watt-hours, before heading into another southern hemisphere Martian winter later in 2017. It will count as Opportunities 8th winter on Mars.
“The science team is really jazzed at starting to see this area up close and looking for clues to help us distinguish among multiple hypotheses about how the valley formed,” said Opportunity Project Scientist Matt Golombek of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California.

NASA’s Opportunity rover scans around and across to vast Endeavour crater on Dec. 19, 2016, as she climbs steep slopes on the way to reach a water carved gully along the eroded craters western rim. Note rover wheel tracks at center. This navcam camera photo mosaic was assembled from raw images taken on Sol 4587 (19 Dec. 2016) and colorized. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com/Marco Di Lorenzo
Meanwhile Opportunity’s younger sister rover Curiosity traverses and drills into the lower sedimentary layers at the base of Mount Sharp.
And NASA continues building the next two robotic missions due to touch down in 2018 and 2020 – as well as focusing its human spaceflight effort on sending humans on ‘Journey to Mars in the 2030s with the Space Launch System (SLS) mega rocket and Orion deep space crew capsule.
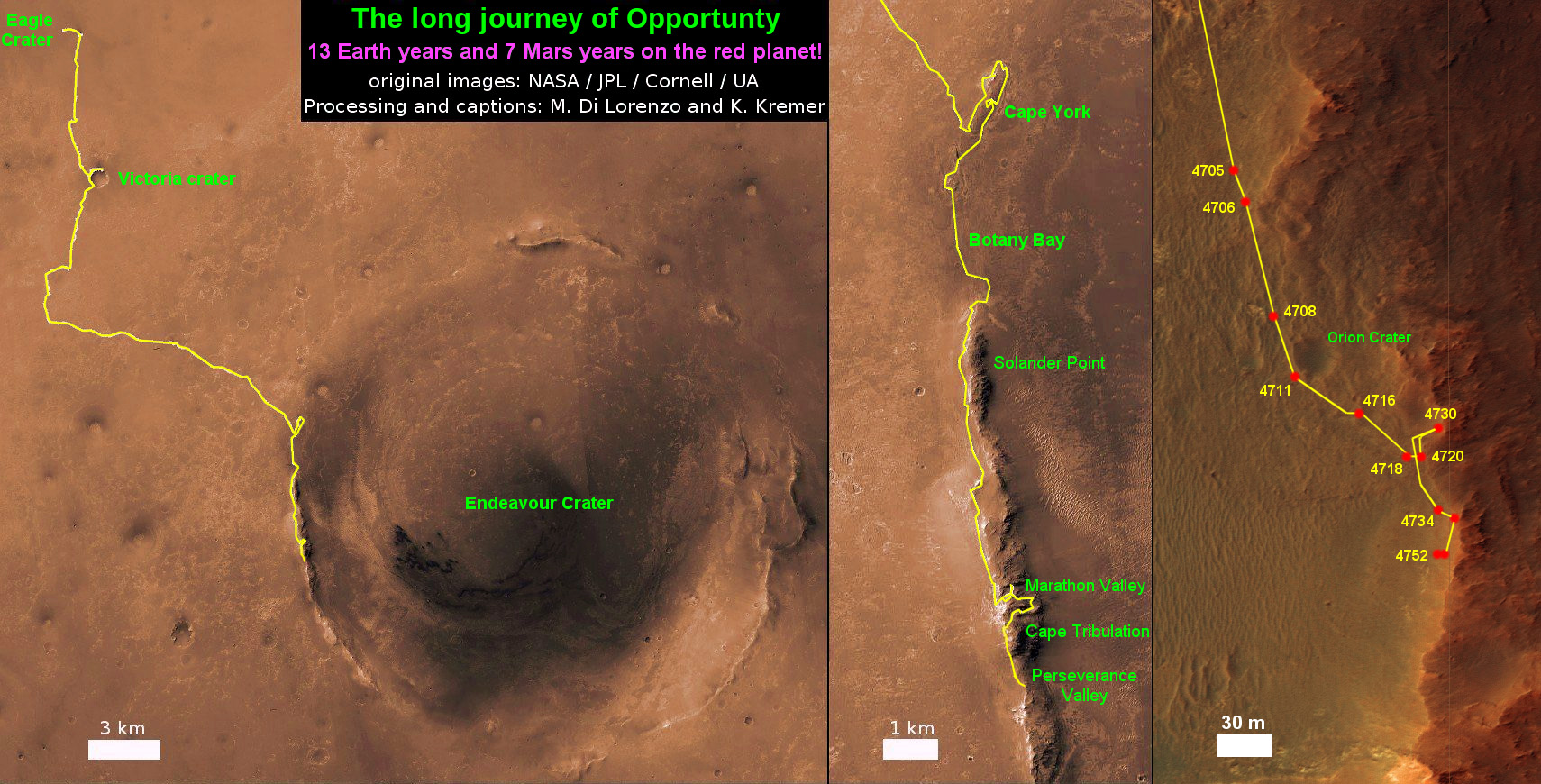
13 Year Traverse Map for NASA’s Opportunity rover from 2004 to 2017. This map shows the entire 44 kilometer (27 mi) path the rover has driven on the Red Planet during over 13 years and more than a marathon runners distance for over 4763 Sols, or Martian days, since landing inside Eagle Crater on Jan 24, 2004 – to current location at the western rim of Endeavour Crater at the head of Perseverance Valley. After studying Spirit Mound and ascending back uphill the rover has reached her next destination in May 2017- the Martian water carved gully at Perseverance Valley near Orion crater. Rover surpassed Marathon distance on Sol 3968 after reaching 11th Martian anniversary on Sol 3911. Opportunity discovered clay minerals at Esperance – indicative of a habitable zone – and searched for more at Marathon Valley. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/ASU/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
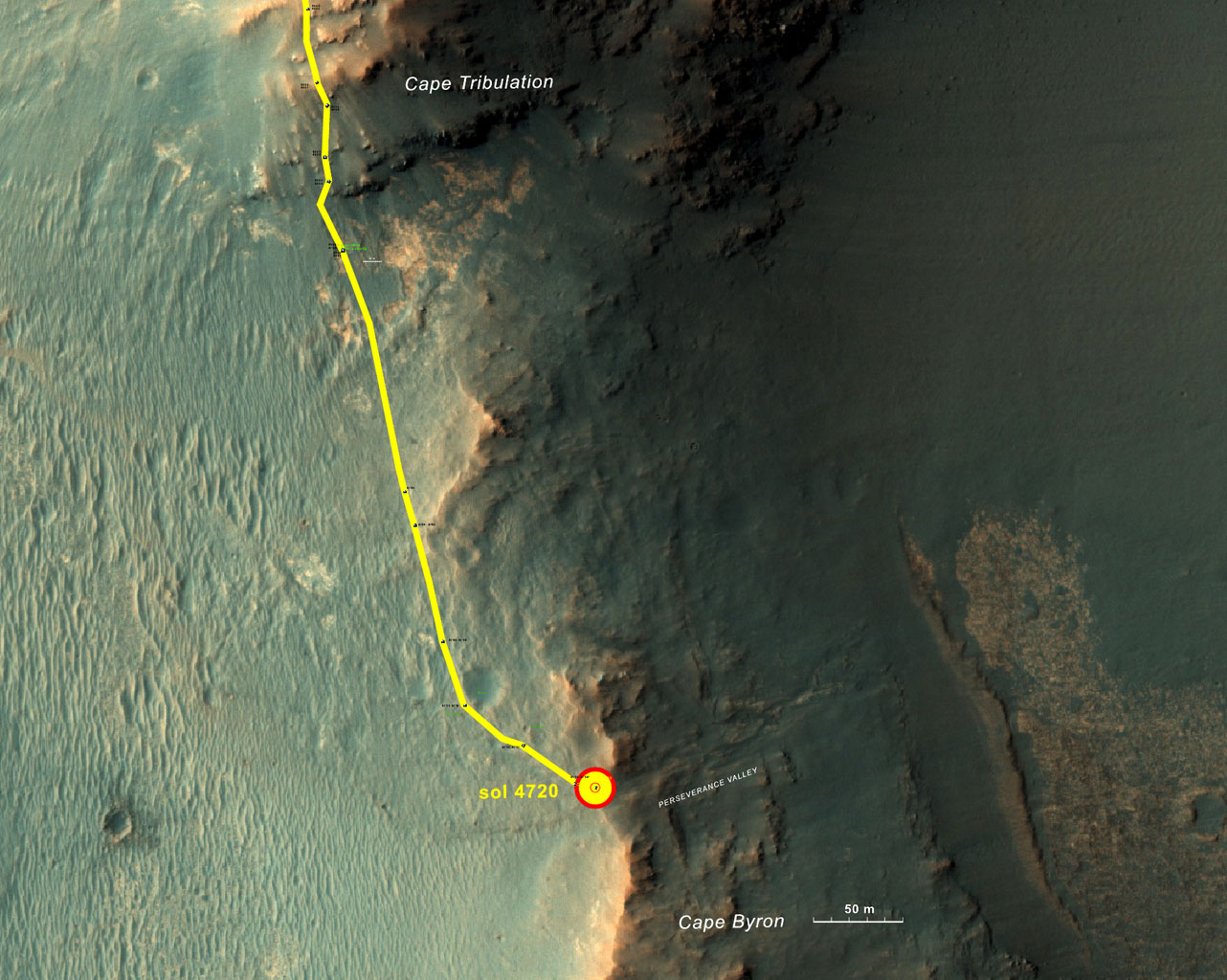
This graphic shows the route that NASA’s Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity drove in its final approach to “Perseverance Valley” on the western rim of Endeavour Crater during spring 2017. Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona/NMMNH
The post Opportunity Reaches ‘Perseverance Valley’ Precipice – Ancient Fluid Carved Gully on Mars appeared first on Universe Today.
Universe Today
Go to Source
Powered by WPeMatico